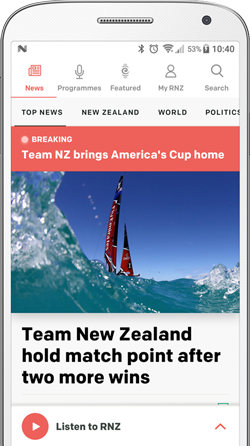
Supporters of the main opposition Republican People's Party (CHP) wave flags during an election rally, ahead of the 28 May presidential runoff vote, in Istanbul, Turkey. Photo: AFP/ Umit Turhan Coskun
By Paul Kirby, BBC News, Ankara
Turks vote on Sunday in a momentous presidential run-off to decide whether or not Recep Tayyip Erdogan should remain in power after 20 years.
His challenger Kemal Kilicdaroglu, backed by a broad opposition alliance, has billed the vote as a referendum on Turkey's future direction.
The president, the favourite to win, promised a new era uniting the country around a "Turkish century".
But the more pressing issue is rampant inflation and a cost-of-living crisis.
Polling stations open at 08:00 (05:00 GMT) and close at 17:00 (14:00 GMT). The big vote from expats, carried out around the world, had already finished.
Turnout in the first round was an impressive 88.8 percent, and Erdogan's lead was 2.5 million votes. Which was why both candidates had their eye on the eight million who did not vote - but could this time.
Ahead of the run-off Kilicdaroglu accused his rival of foul play, by blocking his text messages to voters while the president's messages went through.
Opposition parties have deployed an army of volunteers in a bid to ensure no vote-rigging takes place.
International observers spoke of an uneven playing field after the first round. But there was no suggestion that any irregularities in voting would have changed the result.
Kilicdaroglu promised a very different style of presidency on his final day of campaigning: "I have no interest in living in palaces. I will live like you, modestly... and solve your problems."
It was a swipe at Erdogan's enormous palatial complex on the edge of Ankara which he moved to when he switched from prime minister to president in 2014. After surviving a failed coup in 2016 he took on extensive powers, detained tens of thousands of people and took control of the media.
So it was laden with symbolism when he paid a campaign visit on Saturday to the mausoleum of a prime minister executed by the military after a coup in 1960.
"The era of coups and juntas is over," he declared, linking Turkey's current stability to his own authoritarian rule.
Turkey, however, was deeply polarised, with the president reliant on a support base of religious conservatives and nationalists, while his opposite number's supporters were mainly secular - but many of them nationalist too.

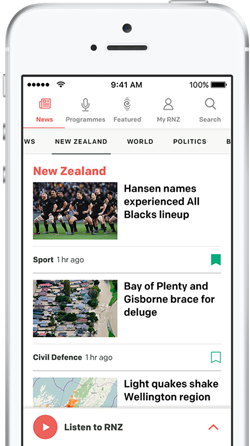
Supporters of Turkish President Tayyip Erdogan hold a flag of his portrait outside the AK Party headquarters in Ankara, Turkey, on 15 May. Photo: AFP/ Adem Altan
For days the two men traded insults. Kilicdaroglu accused the president of cowardice and hiding from a fair election; Erdogan said his rival was on the side of "terrorists", referring to Kurdish militants.
But after days of inflammatory rhetoric about sending millions of Syrian refugees home, the opposition candidate returned to Turkey's number-one issue - the economic crisis, and in particular its effect on poorer households.
A 59-year-old woman and her grandson joined him on stage to explain how her monthly salary of 5000 lira (£UK200; $US250) was now impossible to live on as her rent had shot up to 4000 lira (£UK160; $US200).
It may have been staged, but this is the story across Turkey, with inflation at almost 44 percent and salaries and state help failing to keep pace.
Economists said the Erdogan policy of cutting interest rates rather than raising them had only made matters worse.
The Turkish lira hit record lows, demand for foreign currency had surged and the central bank's net foreign currency reserves were in negative territory for the first time since 2002.
East of Ankara, gleaming tower blocks had been springing up in Kirikkale. It looked like boom-time for this city, run by the president's party.
But many people here were struggling.
Fatma had run a hairdresser's for 13 years but for the past two, work had dried up, and the cost of rent and hair products had soared.
She voted for an ultranationalist candidate who came third, and did not trust the two men left in the race.
A few doors up the street, Binnaz worked a sewing machine at a shop for mending clothes.
People could not afford new dresses so she was earning much more, even if her monthly rent had trebled to to 4000 lira. Despite Turkey's stricken economy, she was putting her faith in the president.
"I believe [Erdogan] can fix it because he's been in power for 21 years and he has all the power. It's his last term [in office] so he'll do all he can for us, " Binnaz said.
Outside a supermarket, Emrah Turgut said he was also sticking with Erdogan because he had no faith in the other option, and believed the president's unfounded allegations that the biggest opposition party co-operates with terrorists.
Turkey's second-biggest opposition party, the HDP, denied any link to the militant PKK, but President Erdogan had used their backing for the rival candidate to suggest a link to terrorists.
Whoever wins on Sunday, Turkey's parliament was already firmly in the grip of Erdogan's Islamist-rooted AK Party and its far-right nationalist ally, the MHP.
The AKP also had the youngest MP, who arrived in parliament on the eve of the presidential vote.
Zehranur Aydemir, 24, believed if he won then he would lay the foundations for a century in which Turkey would become a global power: "Now Turkey has a bigger vision it can dream bigger;" It was another grandiose Erdogan project.
But Turkey's economy is likely to prove a more pressing task, whoever wins the run-off.
-BBC